In a recent exploration of Cardano’s ecosystem, Essential Cardano provided an insightful look at the platform’s native tokens.
Earlier today, Essential Cardano, an open-source, community-driven Cardano content library, shed light on the complexities of Cardano ($ADA) native tokens in a blog post, providing a straightforward explanation of their unique nature and value proposition in the ever-evolving blockchain industry.
In February 2021,the Mary protocol upgrade brought about a significant innovation — Cardano native tokens. Uniquely, these tokens allow digital assets to be minted and transacted directly on the blockchain, a departure from other blockchains that depend on smart contracts for the same purpose. This functionality, states Essential Cardano, offers a more streamlined approach to creating decentralized applications (DApps), cutting down on complexity, cost, and potential human error.
The Cardano blockchain, according to Essential Cardano, can support a diverse array of digital assets, including but not limited to stablecoins, utility tokens, credential tokens, and security tokens. These native tokens extend the accounting infrastructure of the ledger model, enabling simultaneous transaction processing with different kinds of assets. It’s worth noting, however, Essential Cardano points out that there are distinct differences between native tokens and Cardano’s own currency, ADA. Namely, while native tokens can be created and destroyed, ADA cannot, and it is solely ADA that can be utilized for transaction fees and staking rewards.
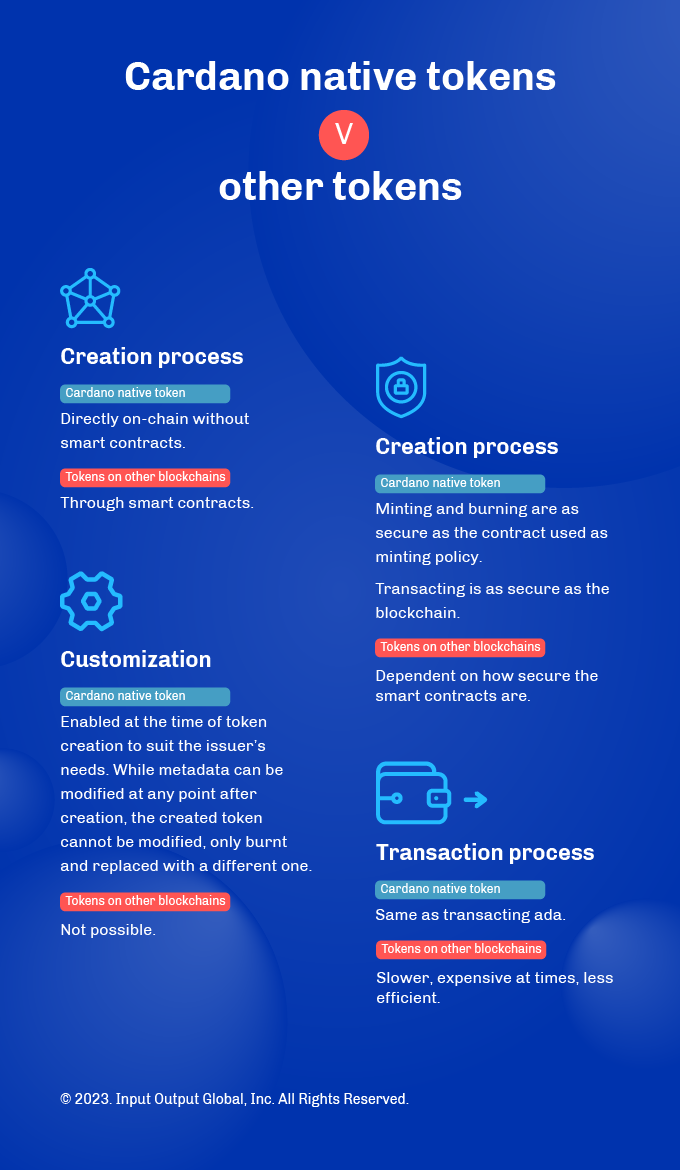
Moreover, Essential Cardano explains Cardano native tokens possess particular attributes that distinguish them from other blockchain tokens. Once a native token is created, it can be transacted in a way similar to ADA. Additionally, the Cardano Transaction Metadata (CMT) feature allows issuers to add bespoke information to their native tokens, such as name, symbol, icon, the number of tokens, Cardano wallet address, and monetary policy.
The blog post outlines various use cases for Cardano’s native tokens, demonstrating their versatility beyond simple value transfer. For instance, within Decentralized Finance (DeFi), native tokens can be used to craft stablecoins, acting as a store of value or a means of payment. In the gaming industry, native tokens can be used to create tradable in-game items on decentralized marketplaces. Additionally, they can be deployed to create, store, and transact unique digital art efficiently and to develop decentralized identities for secure authentication and verification.








